How Does Injection Molding Work – An Introduction
Injection molding is a popular technique used in the manufacturing industry to inject molten materials into molds, solidify them in different shapes, and create spare parts. It is a mass-production technique to create identical plastic parts. A range of components can be manufactured using this technique, be it electronics, automobile components, toys, kitchenware, and more.
Let’s read more about injection molding in this blog.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is the process of injecting molten/ liquid plastic into a mold and clamping it until the liquid cools down and solidifies. Materials like plastic, ceramics, metal, and glass are melted on high heat to turn them into a liquid state. This hot liquid is injected into various molds, which are clamped shut and left to cool down. The molds are then cooled, and the material inside them solidifies, taking their shape. They are then removed from the molds and tested for quality before packaging and delivery.
Creating the mold is the first step of injection molding. Once you have the mold ready, it can be used multiple times to create a huge batch of products. A mold is a hollowed-out block in the shape, size, and dimensions of the final product you want. Additives like color, sparkles, etc., can also be added to the molds while injecting molten plastic into them.
Injection molding has become a popular technique due to its cost-efficiency and ease of use. It is a convenient technique to mass produce large batches of final products in quick time. It also offers flexibility in designs. Additionally, manufacturers can also choose different types of injection molding machines based on their requirements.
A Brief History of Injection Molding
Molding has been a well-known technique since the Second World War days. It is a great method for mass production, which became a necessity during the war. However, the actual history dates back to 1872, when American investors John Wesley Hyatt and his brother Isaiah developed the first machine for injection molding. The machine had a simple design where a piston pushed hot and molten plastic into a mold through a cylinder. This machine was used to produce buttons, combs, etc., in large batches.
A few years later, in 1919, German chemist Arthur Eichengrün created an injection molding press and filed a patent application in 1939 for molding plasticized cellulose acetate. This raw material was less inflammable compared to other materials used back then.
With the onset of World War II, there was an increase in demand for cheap products manufactured in mass production. Since metal was expensive, plastic was used to create spare parts for weaponry and other products. Even after the war ended, plastic continued to be popular among the common public and became a standard product in the global market.
However, the modern-day injection molding machine traces its roots to the gas-assisted unit developed in the 1970s by James Watson Hendry. He also made the first screw injection molding tool during WWII. Nevertheless, the gas-assisted machine made it easier to manufacture intricate parts and reduce the cooling time. This led to faster production.
The latest injection molding machines rely on the same old technique but are powered by computer software to design molds and automate the process. They also improve the quality and accuracy of the end product.
How Injection Molding Works
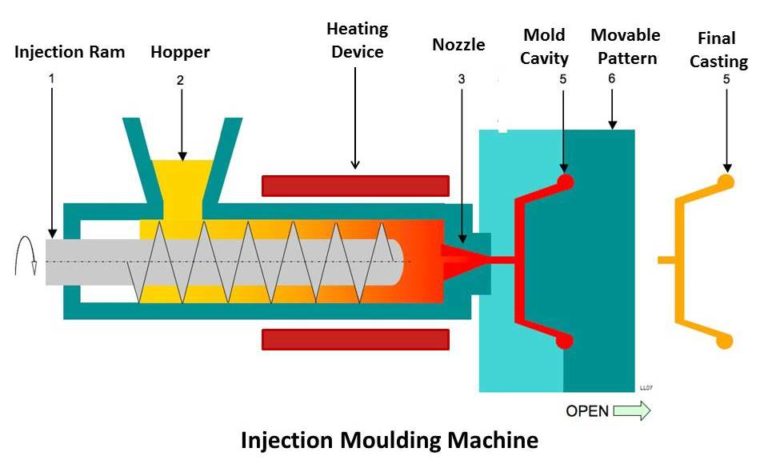
Injection molding is a multi-stage method where every step is crucial. An error or lapse at any step can lead to defective products.
Step 1: The raw material (plastic pellets) is added to a hopper and sent to a cylinder.
Step 2: The cylinder is heated for the plastic pellets to melt and turn into a hot liquid.
Step 3: The nozzle at the other end of the cylinder injects the molten plastic into the mold channel. It works much like a syringe.
Step 4: The mold channel (also known as sprue) will be cooled for the material inside to harden and solidify in its shape.
Step 5: The sprue is removed from the part after cooling down. Finishing touches will be added to the final parts before sending them to the quality check.
Common Defects in Injection Molding
Even though injection molding has many advantages and is a reliable technique for mass production, it is not without a few issues. Not taking proper care during the production cycle can lead to the following defects and affect the overall product quality.
- Cracking
Cracking is a highly common defect in injection molding where the final product develops cracks when removed from the mold. This happens when the mold resistance is greater than necessary. It can be solved by reducing the injection pressure or mold temperature and decreasing the ejection speed.
- Weld Lines
Weld lines are thin streaks on the final product, which affect their strength and lead to faster breakage. They are caused when the liquid cools too quickly in the mold. The weld lines can be prevented by increasing the temperature of the material, increasing the injection speed, or adjusting the pressure on the mold.
- Bubbles
Bubbles are also called voids, which are tiny air holes in the final product. They weaken the final product, resulting in breakage. The bubbles occur when the pressure on the mold is incorrect. However, the issue can be solved by adjusting the mold temperature and pressure, adjusting the gate position, and decreasing the thickness.
- Flashing
Flashes are also known as burrs. They occur when excess plastic seeps out of the mold. Check the quantity to ensure it is not high. Similarly, ensure the injection speed is not too slow or fast and that the molds are not clamped tighter than necessary.
- Sinkage
Sinkage is when the surface of the final product is uneven or sinks due to incorrect pressure applied when molding. It happens when the pressure is inconsistent during the injection process. Nevertheless, it can be avoided by checking the mold for leakage, clogging, contamination, etc. Additionally, the quantity of liquid plastic should also be enough to fill the mold.
Plastics Used in Injection Molding
Over the years, a plethora of plastics have been used by manufacturers to create components using the injection molding technique. The following plastics are more commonly used:
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): It is a common plastic used to make household items, toys, etc.
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET): It is a strong and shatter-resistant plastic used for food and beverage containers.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): It is a multipurpose plastic used in construction materials like plumbing, electrical wiring, flooring, etc.
- Polycarbonate (PC): It is a clear and shatter-resistant plastic used to make medical and safety equipment.
- Polypropylene (PP): It is a heat-resistant plastic used for manufacturing industrial and automotive components.
Benefits of Injection Molding
The injection molding technique offers many advantages, such as the following:
- Mass Production
The biggest benefit of injection molding is its ability to produce the final products in bulk. A large number of items can be continuously created in batches without compromising quality. It’s the best choice to deliver consistent results.
- Versatility
Just about any type of product can be created using this technique. Since the machines are compatible with more than one material, manufacturers find it easy to make products in varying sizes, colors, shapes, designs, etc.
- Cost Efficiency
The injection molding technique is budget-friendly compared to other molding methods. The manufacturer can choose the type of machine that fits their budget and production needs. Moreover, the materials can be reused to minimize wastage.
- Precision and Repeatability
Precision and repetition are two variables to consider during bulk production. Injection molding offers both and is still easy to use. Even though molds wear down and need to be replaced, each aluminum mold can easily last 5,000 to 10,000 cycles.
- Appealing Appearance
How the final products look is also an important factor. Fortunately, the items made through injection molding are ready for delivery. They need little to no finishing touches and can be packaged and shipped after quality control.
Applications of Products Made Through Injection Molding
As mentioned earlier, a variety of products can be made using injection molding. This technique is widely used in the following industries:
Automotive (creating spare parts and components for vehicles)
Toys (the parts for dolls, action figures, etc., are made through this process)
House and Kitchenware (plastic curtains, hangers, hooks, spatulas, bowls, glasses, cups, and many more)
Electrical Components (plugs, switches, screw holders, etc.)
Medical Devices (stethoscopes, syringes, etc.)
Food and Beverage Containers (instant noodle cups, yogurt cups, bottles, etc.)
Tools (screwdrivers, hammers, wrenches, etc.)
Sporting Items (tennis balls, hockey pucks, etc.)
Conclusion
Injection molding is a versatile, precise, and reliable technique to mass-produce numerous products in different industries. Work with a reputed partner to access state-of-the-art injection molding equipment powered by the latest technology.
Contact Trumold for customized injection molding services with greater precision, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.




